
Scripts are sequences of commands, often written in programming languages like Python or Bash, that automate computer tasks. Specifically, they can sort and organize files by moving, copying, renaming, or deleting them based on rules defined in the script. Unlike manually organizing files, scripts handle repetitive actions quickly and consistently by following your precise instructions, such as grouping files by type, date, or keyword.
For example, a Python script could organize a chaotic downloads folder daily, moving .pdf files to a "Documents" directory and .jpg files to "Images." On a Mac, an Automator workflow script might batch-rename hundreds of photos using a date prefix. Data analysts often use scripts to sort log files by timestamps for troubleshooting, while content creators use them to arrange project assets.
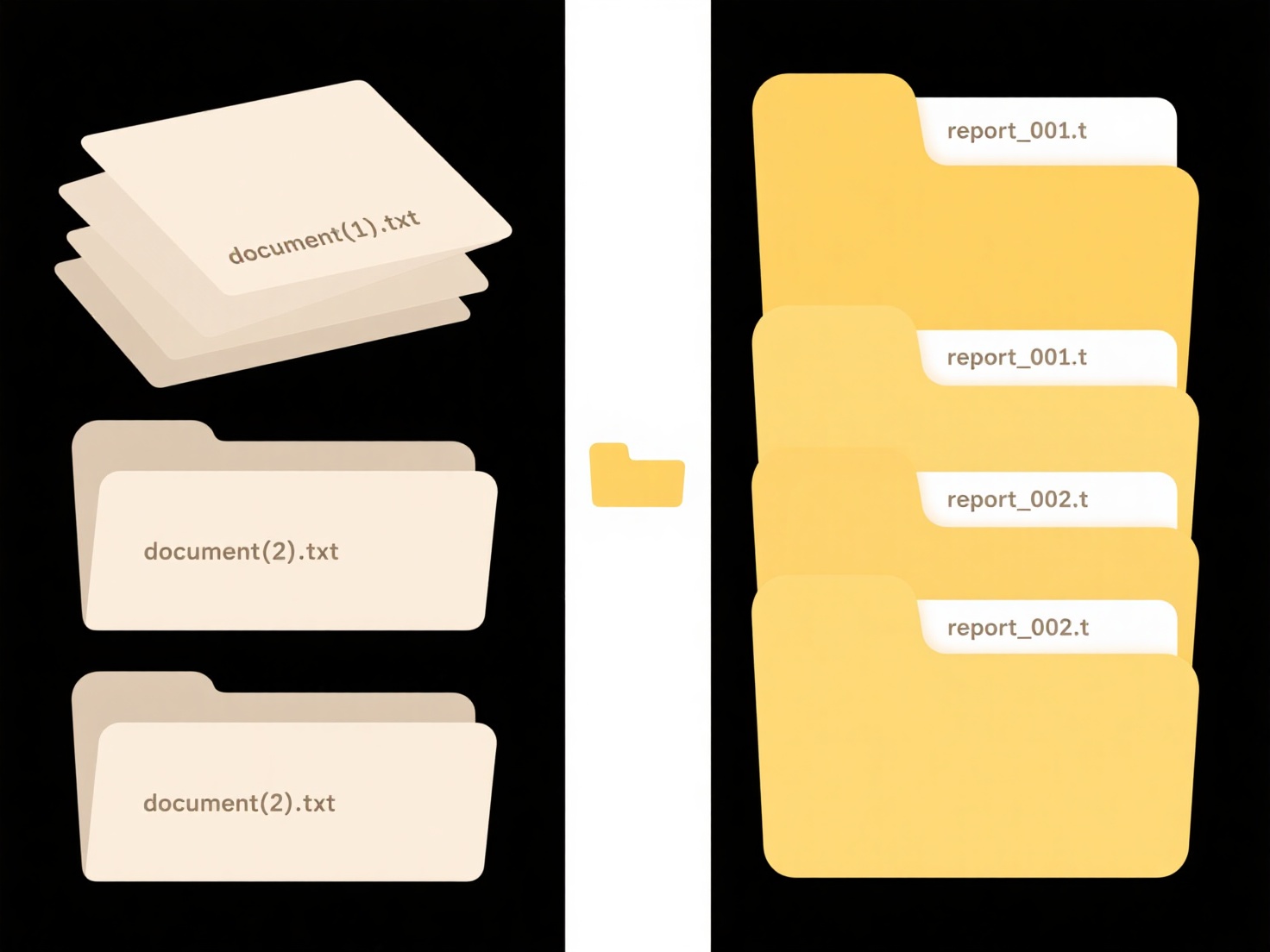
The major advantage is vast time savings and elimination of manual errors for recurring tasks. Key limitations include the initial learning curve to write scripts safely and the risk of errors (like mis-sorting or deleting files) if the script logic is flawed. Future developments involve AI-powered tools generating scripts from natural language prompts, lowering the barrier to entry and accelerating adoption across non-technical users.
Can I use scripts to sort and organize files?
Scripts are sequences of commands, often written in programming languages like Python or Bash, that automate computer tasks. Specifically, they can sort and organize files by moving, copying, renaming, or deleting them based on rules defined in the script. Unlike manually organizing files, scripts handle repetitive actions quickly and consistently by following your precise instructions, such as grouping files by type, date, or keyword.
For example, a Python script could organize a chaotic downloads folder daily, moving .pdf files to a "Documents" directory and .jpg files to "Images." On a Mac, an Automator workflow script might batch-rename hundreds of photos using a date prefix. Data analysts often use scripts to sort log files by timestamps for troubleshooting, while content creators use them to arrange project assets.

The major advantage is vast time savings and elimination of manual errors for recurring tasks. Key limitations include the initial learning curve to write scripts safely and the risk of errors (like mis-sorting or deleting files) if the script logic is flawed. Future developments involve AI-powered tools generating scripts from natural language prompts, lowering the barrier to entry and accelerating adoption across non-technical users.
Related Recommendations
Quick Article Links
What is a .tiff file used for?
A TIFF file (Tagged Image File Format) stores high-quality raster images using lossless compression, preserving all orig...
How do I enforce unique file naming in shared spaces?
Unique file naming in shared spaces means establishing rules or using tools to prevent collaborators from saving files w...
How do I name files for easier searching?
File naming conventions standardize how files are labeled to improve searchability. Effective names are descriptive, con...